Implicit Identity Leakage: The Stumbling Block to Improving Deepfake Detection Generalization
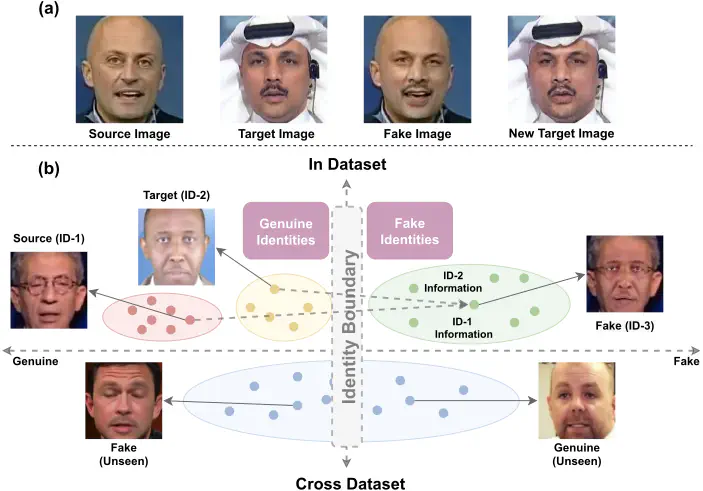 The Implicit Identity Leakage phenomenon.
The Implicit Identity Leakage phenomenon.Abstract
In this paper, we analyse the generalization ability of binary classifiers for the task of deepfake detection. We find that the stumbling block to their generalization is caused by the unexpected learned identity representation on images. Termed as the Implicit Identity Leakage, this phenomenon has been qualitatively and quantitatively verified among various DNNs. Furthermore, based on such understanding, we propose a simple yet effective method named the ID-unaware Deepfake Detection Model to reduce the influence of this phenomenon. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art in both in-dataset and cross-dataset evaluation.
Type
Publication
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2023)